Magadh Empire
- The Magadha Empire was a significant kingdom in ancient India, ruled by various great leaders. It’s during this time that religions like Jainism and Buddhism thrived.
- Three main dynasties governed Magadha: the Shishunaga, Haryanka, and Nanda Dynasties. The empire was founded by Jarasandha.
- The Magadha Empire existed from 684 BCE to 320 BCE.
- Between the 6th and 4th centuries BCE, four major Mahajanapadas, including Magadha, competed for power.
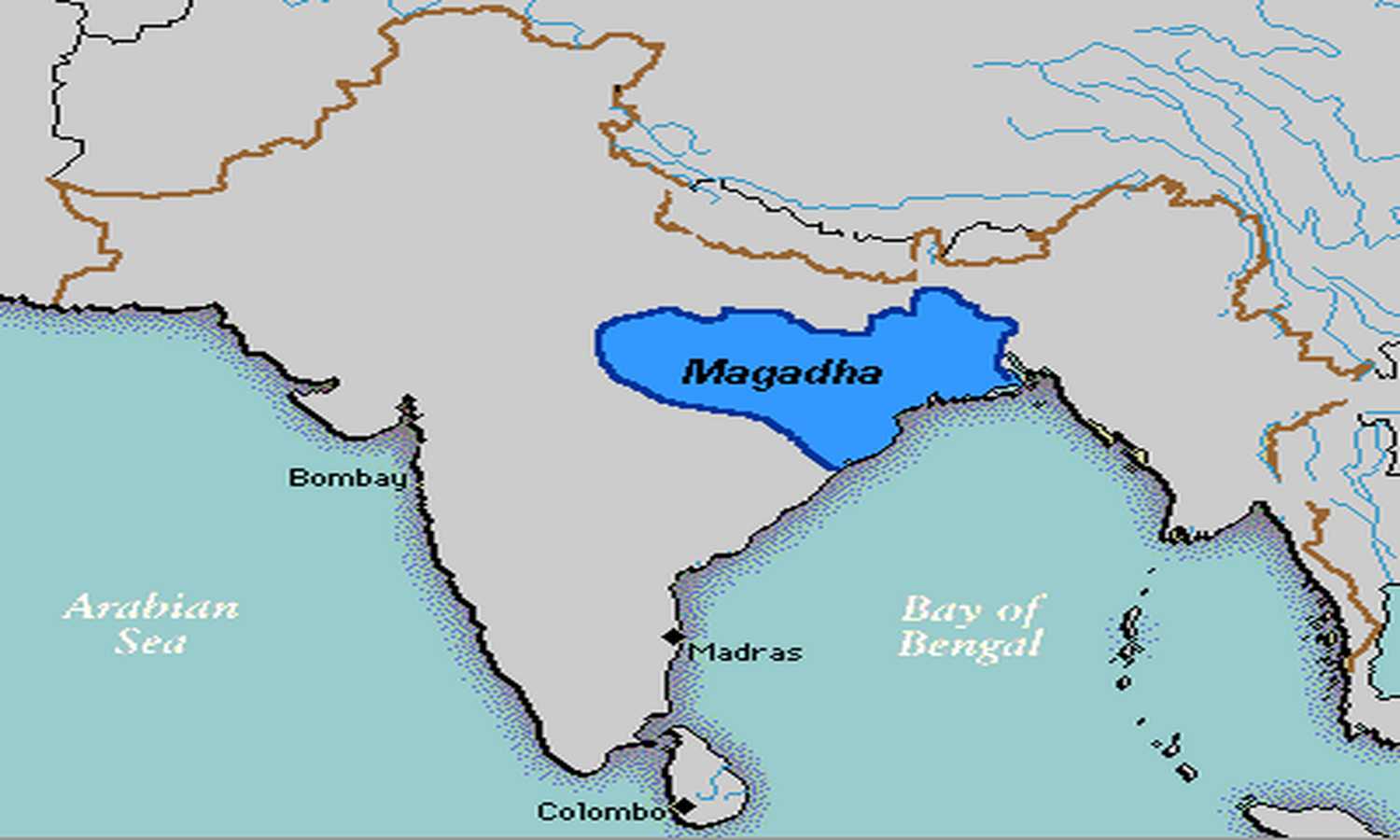
- Magadha succeeded in becoming a powerful state and the most dominant one in ancient India. Magadha was located in what is now Bihar.
Founder Of Magadh Empire
- In the Mahabharata, it’s mentioned that Jarasandha, a descendant of Brihadratha, established a big empire in Magadha.
- He’s credited with founding this powerful Magadha empire. Many of the Mahajanapadas were ruled by kings or groups of kings, often called ganas or sanghas. Oligarchy power, like sanghas, was seen in Vaishali.
- Magadha became the most powerful Mahajanapada due to its strategic location.
- During Buddha’s time, the Indian subcontinent had sixteen large states called ‘Mahajanapadas.’
- The term ‘Janapadas’ means the land where people settle.
- These large states were mainly in the northern part of the subcontinent, stretching from the northwest to Bihar.
- They included well-known Mahajanapadas like Vatsa, Vajji, Kuru, Magadha, Koshala, Gandhara, Panchala, and Avanti.
More Information On The Magadha Empire
Between 684 B.C. and 320 B.C., the Magadha Empire ruled over India. The ancient Hindu epics, Ramayana and Mahabharata, also mention this empire. It was governed by three dynasties from 544 BC to 322 BC.
- The first dynasty was the Haryanka Dynasty, ruling from 544 BC to 412 BC.
- The second dynasty was the Shishunaga Dynasty, which ruled from 412 BC to 344 BC.
- The third dynasty was the Nanda Dynasty, ruling from 344 BC to 322 BC.
Haryanka Dynasty
In the Haryanka Dynasty, Bimbisara was one of the early rulers of the Magadha Empire. He played a significant role in its growth, absorbing the kingdom of Anga to the east and contributing to the foundation of the Mauryan empire. Bimbisara is also known for his cultural achievements and efficient administrative system, with high-ranking officials divided into three categories: Executive, Military, and Judiciary.
Shishunaga Dynasty
The Shishunaga Dynasty ruled the Magadha Kingdom in ancient India from 413 BCE to 345 BCE. It was the third imperial dynasty in Magadha, coming after the Brihadratha and Haryanka Dynasties. Shishunaga, an “amatya” or minister of the last Haryanka emperor, founded this dynasty.
During the 5th century, Shishunaga became the first king of this dynasty after a series of revolts against the Haryanka Dynasty. The Shishunaga Dynasty laid a strong foundation for the Magadha Empire and had the potential to rule India for many years. Their inheritance of valuable land and wealth boosted their chances for growth and prosperity.
Nanda Dynasty
Between the 4th and possibly 5th centuries BCE, the Nanda Dynasty ruled the northern part of India. They started in eastern India (the Magadha region) by replacing the Shishunaga dynasty and later expanded their control over a larger part of northern India. The Nanda rulers have different names and legacies in various ancient accounts.
From 343 to 321 BCE, the Nanda dynasty governed Magadha in northern India. Their capital was in Pataliputra, located in the eastern part of India, which is modern-day Patna.
The Nandas made contributions to fields like Sanskrit drama, Buddhist and Jain traditions, following the footsteps of their predecessors from the Haryanka and Shishunaga dynasties. History shows that the Nandas prospered due to the adoption of a new currency and taxation system.
However, the Nandas weren’t popular among their subjects because of their bad behavior, low social status, and high taxes. The founder of the Mauryan Empire, Chandragupta Maurya, and his advisor Chanakya, eventually overthrew the last Nanda ruler, Mahapadma.
Important Kings Of Magadha Empire
The Magadha Empire had several powerful kings from the Haryanka Dynasty, including Bimbisara, Ajatashatru, and Udayin.
Bimbisara:
- Ruled the empire for 52 years, from 544 B.C. to 492 B.C.
- Strengthened his empire through matrimonial alliances, including marriages to Kosaladevi, a princess from Kosala, and Chellana, a princess from the Licchavi family of Vaishali.
- Married Khema from the royal house of Madra in central Punjab and annexed the Anga empire, establishing friendly relations with Avanti.
Ajatshatru:
- Son of Bimbisara, he became king by overthrowing his father.
- Focused on expansion during his rule, extending control over Kashi and Koshala.
- Resolved disputes with Koshal king through a marriage alliance, which included his daughter and Kashi.
- Engaged in a sixteen-year war with the Lichchavis of Vaishali, eventually capturing Vaishali.
- Initially influenced by Jainism, he later supported Buddhism and claimed to have met Gautama Buddha. He supported the construction of chaityas and viharas.
- Attended the First Buddhist Council at Rajagriha after Buddha’s death.
Udayin:
- Eldest son of Ajatashatru, he succeeded as the emperor.
- Established Pataliputra as the new capital, shifting it from Rajagriha.
Naga-Dasak:
- The last ruler of the Haryanka dynasty.
- Faced dissatisfaction from his subjects, leading to his forced abdication.
- The people supported minister Shisunaga for the coronation.
Rise Of Magadha Empire
The rise of the Magadha Empire was influenced by several factors during that time, making it a significant political and cultural power. Here are the reasons behind its development:
Geographical Factors:
- The capital city of the Magadha Empire, Rajagriha, had natural fortifications with five hills.
- Pataliputra, also a capital city, was strategically located at the confluence of the Ganga, Son, Gandak, and Ghagra rivers, facilitating communication, defense, trade, and commerce.
- The empire had abundant resources and fertile land. The surrounding dense forests provided elephants for the army.
Political Factors:
- Magadha was ruled by powerful leaders like Bimbisara, Ajatashatru, and Mahapadma Nanda, known for their effective administration and the use of elephants in their armies.
- The empire had a formidable army with various weapons and a strong defense system.
Cultural Factor:
- Magadha had a unique cultural background with the influence of Buddhism and Jainism, leading to a philosophical outlook.
- The empire did not adhere to the rigid Brahmanical beliefs and rituals, which created a distinct cultural identity.
Economic Factor:
- Magadha possessed significant copper and iron resources.
- Its strategic location supported trade and commerce.
- The large population contributed to agriculture, military service, mining, and city construction.
- The rise of Magadha as a paramount political power was a result of its strong administration, economic stability, and control over important trade routes, especially the Ganga river.
- It competed with other major regions like Kosala, Avanti, and Vatsa, eventually becoming the most powerful and stable state in ancient India. Jarasandha, a descendant of Brihadratha, is credited as the founder of the Magadha Empire.
Magadha Empire GK MCQs With Answer & Explanation in English



Leave a Reply